Latest update: April 28, 2025
Have you received a “Page Indexed Without Content” error alert in Google Search Console?
This error is quite rare, but it’s definitely worth your attention. It implies that Google managed to process and index your page without finding or reading the content.
Your site won’t perform well in the results when facing this error. So, keep reading and learn how to fix it!
Main Causes of “Page Indexed Without Content” Error
The “Page Indexed Without Content” error appears in GSC when Google indexes your resource but cannot retrieve or display its content. Basically, the page exists in Google’s index but the data is missing or unreadable.
This error can negatively affect search rankings. Your resource won’t rank properly if browsers perceive it as empty or lacking valuable information.
Resources with this error might still appear in the results, but people will see them as empty or incomplete. It can lead to poor engagement and much higher bounce rates.
Here are the main causes of the “Page Indexed Without Content” error.
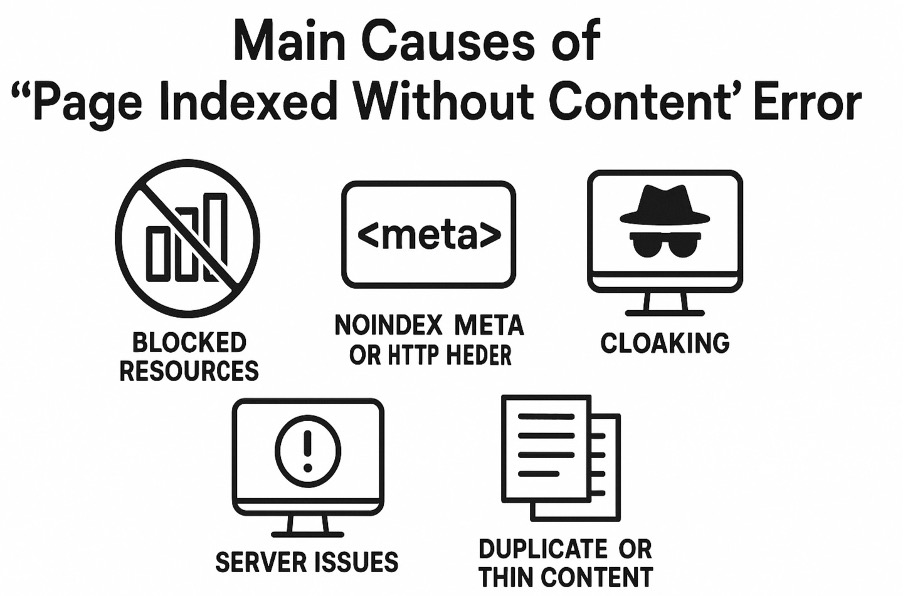
Blocked Resources
Most modern sites rely on JavaScript to render content. If Googlebot can’t access or execute JavaScript, it may fail to load the actual content. As a result, you get an empty page.
This problem might appear because of robots.txt restrictions or incorrect implementation of lazy loading.
Misconfigured frameworks may also lead to this error. This includes
- Client-side rendering issues;
- Missing SSR;
- Delayed content injection.
Noindex Meta Tags or HTTP Headers
Meta tags and HTTP headers determine how search engines interpret your site. Wrong commands might confuse Google about your visibility or content.
For example, Google might not treat your resource correctly if it has a “noindex” tag.
Conflicting meta tags, like “follow” or “noarchive”, may also become a problem. They confuse browsers and lead to indexing difficulties.
The X-Robots-Tag that overrides HTML meta tags also stops Google from showing your materials.
Cloaking
Cloaking can cause a “Page Indexed Without Content” error as well.
It’s the process of showing different content to browsers and users. Sometimes, it might be intentional, but misconfigurations lead to indexing issues.
For instance, sometimes, you might need to show different materials based on user-agent detection. Yet, this can mistakenly hide your content from Googlebot.
Incorrect CDN parameters or geographical limitations may also block access for the web crawler.
Server Issues
Server disruptions can lead to a “Page Indexed Without Content” error.
If a server takes too long to respond, Google may time out before retrieving the content.
HTTP errors also restrict its operations. These include
- 403 Forbidden response;
- 500 Internal Server Error.
Plus, you might cause indexing difficulties by setting inaccurate cache rules.
Duplicate or Thin Content
Google prioritizes indexing pages with original and informative content. Your resource may be categorized “without content” when it’s lacking from this perspective.
This problem is quite common for
- System-generated resources;
- Duplicates;
- Empty pages with CMS malfunctions.
Steps to Fix “Page Indexed Without Content” Error
You already know where to find the “Page Indexed Without Content” error in the Google Search Console. Now, we want to tell you which steps you should take to handle this problem.
Step 1: Find “Page Indexed Without Content”
First, you need to open the GSC and sign in with your Google account credentials. Select the correct website property from the list if you’re managing multiple sites. Also, make sure to verify ownership of the property.
Next, go to the Indexing section in the left sidebar. Click on “Pages” to access the report.
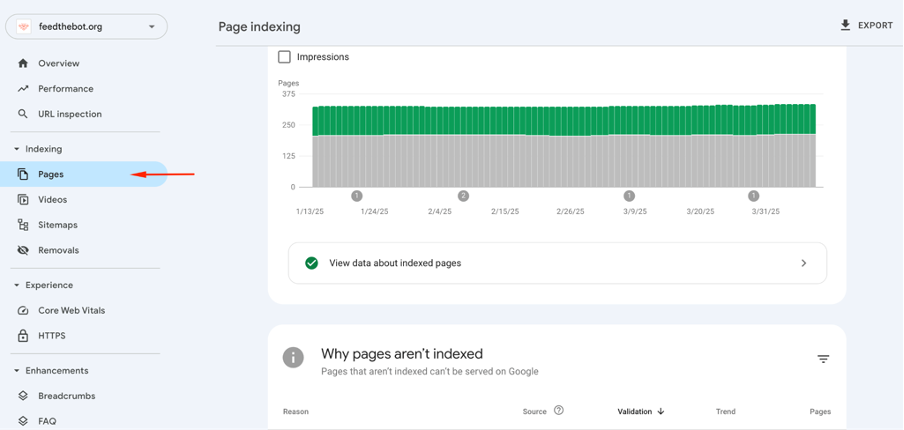
You will see information about all your indexed and non-indexed resources in this report. Plus, it highlights the indexing status over time and any issues that appear.
Scroll down to the Why pages aren’t indexed area. Then find the distinctive entry labeled
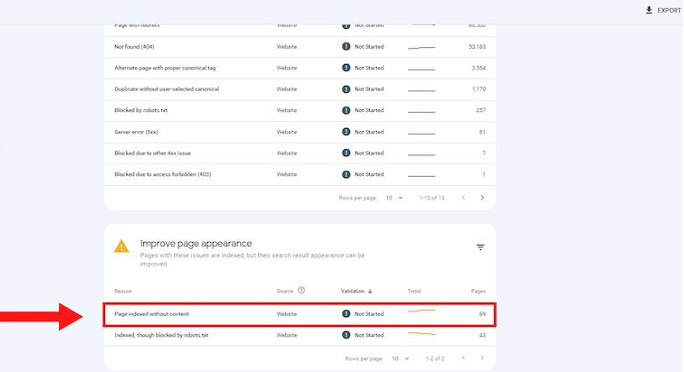
“Page Indexed Without Content” and click on it.
Step 2: Verify Content Accessibility
Start with assessing your page’s accessibility. You can approach it in different ways.
Try opening the involved resource in your browser to validate that it loads correctly and displays the expected content.
Also, you might use the URL Inspection Tool to check how Googlebot sees your site.
Next, we suggest you test for diverse devices and networks to rule out local connectivity disruptions.
Step 2: Check for Blocked Resources
Google needs access to CSS, JavaScript, and images to index a page correctly. So, you need to check if these resources are blocked.
First, review your robots.txt file and check for Disallow tags. Modify these rules to allow access to essential resources if necessary.
Next, you can use Google’s Lighthouse tool to test how mobile-friendly your site is. It helps you determine if Googlebot can render your page.
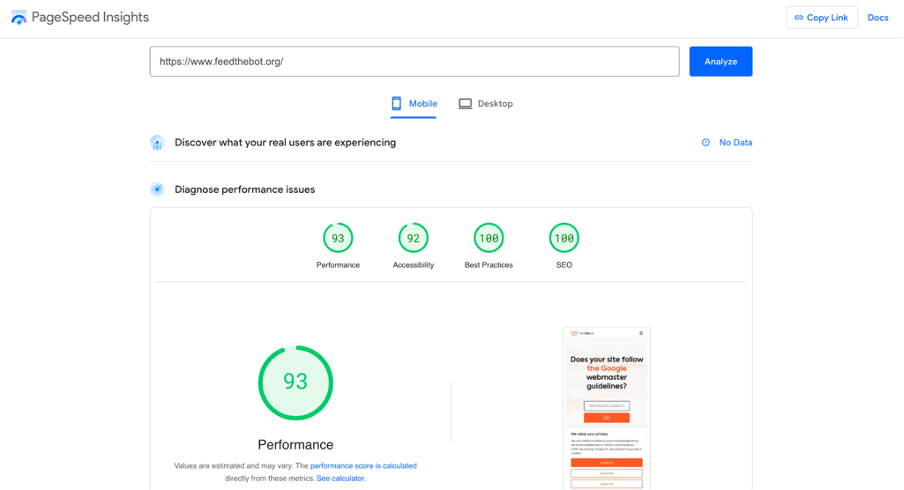
Plus, you can try checking your source code to confirm that the expected text content is present.
Step 3: Fix Issues with JavaScript-Rendered Content
Google has limitations when it comes to rendering JavaScript-heavy resources. So, if you’re using dynamic loading, follow these steps:
- Test rendering through URL Inspection Tool;
- Use “Developers Tools” to scan for JavaScript malfunctions;
- Employ SSR or dynamic rendering to confirm the indexing of static versions.
Step 4: Resolve Server and Hosting Problems
We’ve mentioned before that certain server issues may lead to a “Page Indexed Without Content” error. Here are the steps to complete if that’s the case.
Check your HTTP status code and ensure it returns a 200 OK status.
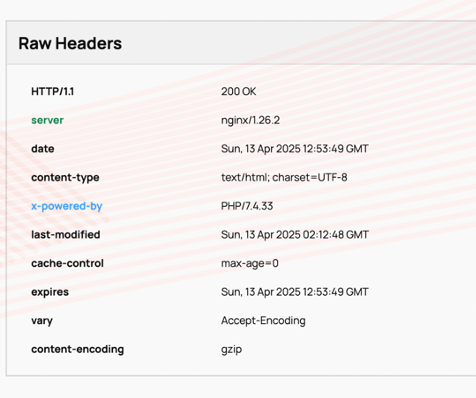
Next, we advise you to review server logs for signs of ongoing delays or errors. Also, consider advancing hosting or optimizing your server setup for faster loading times.
Run uptime tests and change your hosting solution if needed.
Step 5: Review Canonical Tags and Duplicate Content
Improper use of canonical tags often leads to indexing issues. So, make sure you set them right.
For example, if you have multiple versions of the page, specify a preferred version.
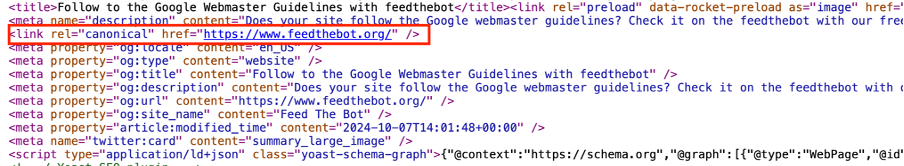
Try to minimize unintended duplicates, as they make Google ignore one version. You have to use 301 redirects or proper URL structures to manage them. Also, make sure that your CMS is not generating duplicate resources with different URLs.
Step 6: Change the Structure of Your Page
Sometimes, the structure of your page may affect indexing. Google may struggle to extract the relevant information if it’s too complex.
You can fix it by following these tips:
- Simplify layouts;
- Use semantic HTML;
- Avoid hidden content (check tabs, accordions, or expandable sections);
- Optimize internal linking;
- Implement schema markup where appropriate.
Also, ensure your content is within the initial HTML document structure.
Step 7: Request Reindexing
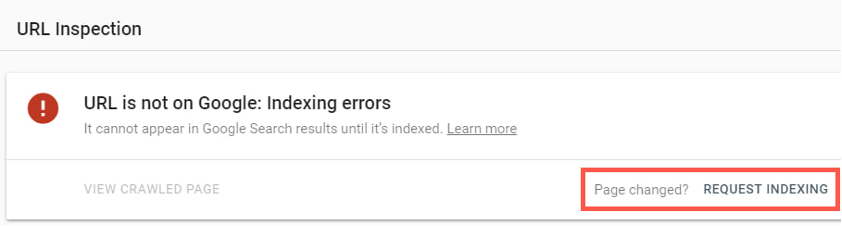
The last step you have to take after solving all the problems is to request indexing.
Go back to your Google Search Console and test the page through URL inspection again. Click on the “Request indexing” button to prompt Google to re-run the crawl.
If you experienced a “Page Indexed Without Content” error with more than one resource, submit the updated sitemap to GSC.
Also, check the “Indexing” report periodically to confirm the resolution of this error. Remember, that Google may take time to re-run modifications. So, monitor indexing progress over the next few days or weeks.
Try to improve the crawl frequency by updating your site with fresh content and strengthening internal linking structures.
Key Takeaways on Fixing Page Indexed Without Content
- A “Page Indexed Without Content” error is not that common. Still, it stops Google from processing and crawling your resources;
- Common causes for this error include cloaking, server issues, restrictive rules, and more;
- To resolve this problem:
- Check for blocked resources.
- Fix JavaScript and server issues.
- Update the structure of your page.
- Avoid duplicates.
- Use canonical tags appropriately.
If you encounter other errors, refer to our Google Search Console guidelines to resolve them.


