Latest update: June 20, 2025
The “Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)” error appears in GSC when Googlebot is forbidden from accessing your URL. It means the server understood your request, but refuses to authorize it.
As a result, Google can’t crawl and index your pages, and they won’t appear in the results. Keep reading and learn how to diagnose and handle this error!
Reasons behind “Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)”
You’ll see the “Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)” error in Google Search Console if Googlebot can’t access specific pages on your site. This error might negatively impact your visibility and indexing. It usually leads to lower rankings or even complete exclusion from results.
You need to identify the root causes of this issue to manage it adequately.
Improper Robots.txt Rules
Misconfiguration in the robots.txt file is a typical cause for a “Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)” error in GSC. This file has instructions for search engine crawlers about which parts of a site they can access.
If you mistakenly include restrictive rules, Googlebot might stop indexing your entire resource.
Access issues might also appear if you block important directories or specific URLs without realizing their value. Plus, misconfigured wildcard rules or case sensitivity errors can block more pages than intended.
Server or Firewall Restrictions
Security plugins and firewalls protect your site from hostile bots and attacks. However, they might incorrectly identify Googlebot as a threat.
Some security configurations include automatic bot detection mechanisms that restrict high-frequency requests. It also leads to access denial for Google.
Plus, a hosting provider may implement server rules that block all bot traffic, including legitimate crawlers.
IP Blocking in .htaccess or Server Configuration
You’ll often have to modify .htaccess or httpd.conf files to improve security or restrict access from unwanted users.
Yet, if you include Googlebot’s IP addresses in the blocked list, it will lead to a “Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)” error.
Outdated or overly aggressive security settings might fail to differentiate between harmful crawlers and legitimate bots.
Authentication Requirements
Your site might require login credentials to access certain pages, like:
- Admin panels;
- Membership-only areas;
- Paywalled content.
Googlebot won’t process them, leading to a 403 error.
Basic HTTP authentication or SSO systems may also inadvertently disrupt indexing. Plus, pages requiring CAPTCHA validation can further restrict automated access.
Incorrect File Permissions
Every site has a structure of files and directories with specific permissions that determine who can read or execute them. If your file permissions are too restrictive, Googlebot may not have the possibility to access certain files.
This issue often appears when you mistakenly set permission levels too low while trying to enhance security.
Hosting providers or CMS may also automatically adjust permissions during updates. They unintentionally restrict access to the crawlers.
CDN or DDoS Protection Blocks
CDNs and security tools that handle DDoS attacks often use automated blocking mechanisms. They might classify Googlebot’s behavior as suspicious because of
- Rapid crawling;
- High request frequency;
- Unusual geographic pattern.
As a result, it may be blocked.
Similarly, some security plugins automatically flag Googlebot as a potential threat based on preset filtering rules.
Fixing the “Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)” Step-by-Step
You already know that the “Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)” error may affect your visibility in search results. Different factors and limitations may trigger this issue.
Now that you have a list of affected pages, we can talk about resolving the problem. Follow the steps we outlined below!
Step 1: Locate the Error in GSC
It’s pretty easy to find pages affected by the “Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)” error within Google Search Console.
Start by logging into your profile. Pick the property you’re interested in if you have more than one site. Open the “Indexing” unit in the menu and click on “Pages”.
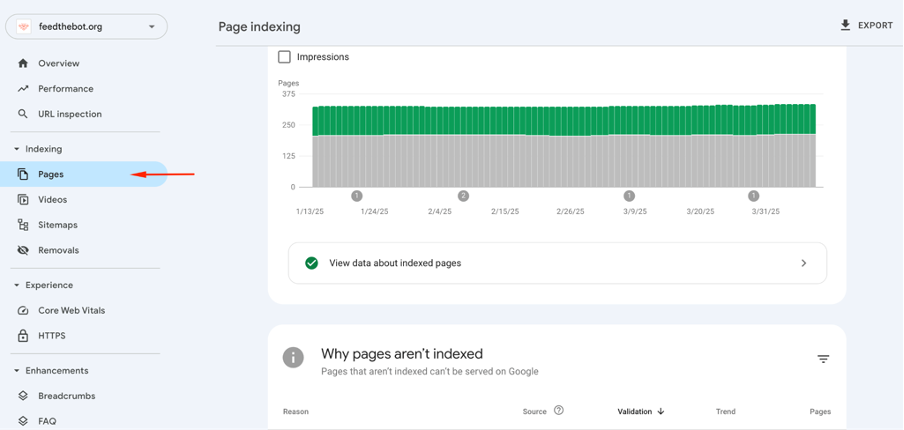
It will show you the indexing status of each page on your site.
Keep scrolling to find a report with all the indexing problems you currently have. You will see it within the ‘Why pages aren’t indexed’ section. Look for a notification about the “Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)” error.
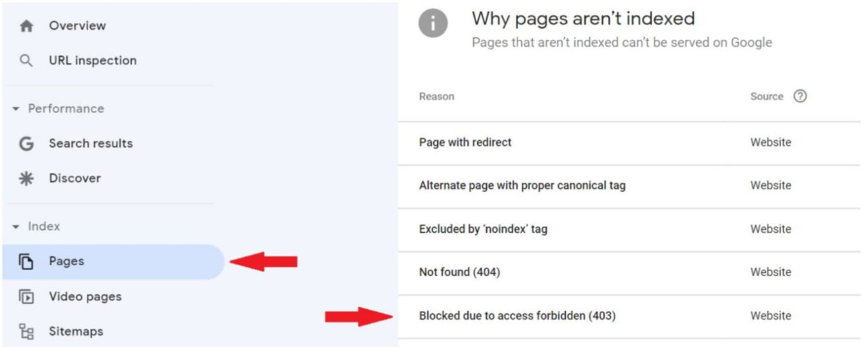
After clicking on this alert, you’ll get a list of all pages involved and a visualization in the form of a graph. You can export this list for further analysis.
Step 2: Verify Googlebot Access
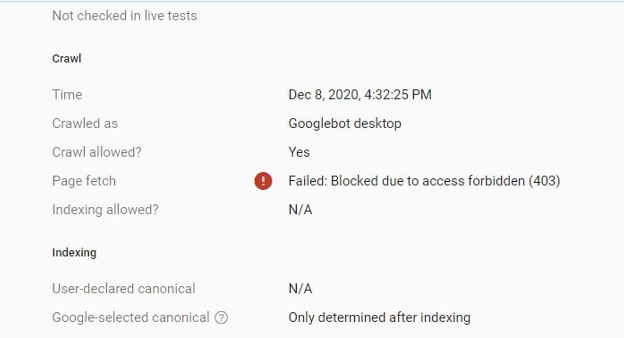
Before you start making any changes, you need to confirm that Googlebot is actually being blocked from crawling your site.
You can use the URL Inspection Tool within GSC. Just enter the affected URL and check if Googlebot can access it. If you see a 403 status, it confirms an access restriction.
Also, you can try out the Lighthouse tool for checking mobile-friendliness. This tool attempts to fetch your page as Googlebot would. If it fails, it’s a signal of blockage.
Last, review your site’s access logs to check for 403 status codes associated with Googlebot’s user agent.
If any of these tests confirm that Googlebot is blocked, complete the next steps to handle the problem.
Step 3: Update Your Robots.txt File
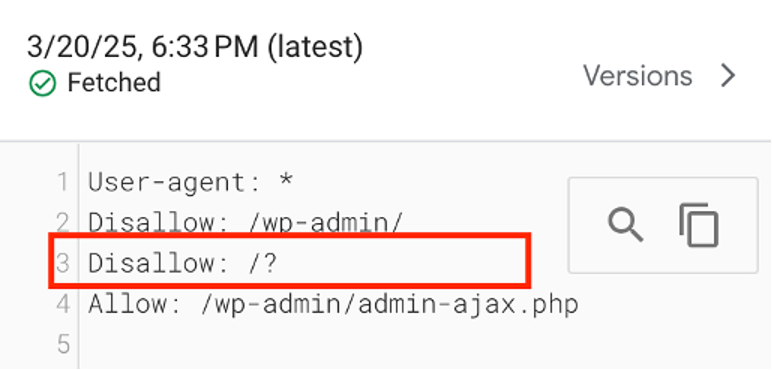
We’ve mentioned above that your robots.txt file dictates which parts of your site search engines can access. Its misconfiguration stops the crawling process for critical pages.
You need to check it for any restrictive rules. To do that, enter your domain name with /robots.txt. If there’s a Disallow: / for all user agents, you need to remove or modify it appropriately.
Next, use GSC’s robots.txt Tester to validate any changes before saving the updated file.
Finally, you can submit the file in GSC to inform Google of the changes.
Step 4: Change Server and Security Settings
Misconfigured .htaccess rules may deny access to search engines. So, look for lines like “Deny from all” or specific rules blocking Googlebot’s IP addresses. You’ll need to remove them if necessary.
Next, you need to review your firewall settings. Check if any security rules are limiting Googlebot. You can whitelist its IP ranges to prevent accidental blocking.
In case you suspect a firewall issue, disable it temporarily and test for access. If the error disappears, re-enable the firewall and configure it to allow Googlebot.
Step 5: Fix File and Directory Permissions
Another thing to do is to review your file permissions. So, connect to your server and verify that:
- Files are set to 644;
- Directories are set to 755;
You can use the chmod command in SSH or adjust permissions through an FTP client.
Also, make sure to update the directory ownership settings if they’re incorrect.
Step 6: Handle Plugin Limitations
WordPress plugins, like Wordfence or Sucuri, may block bots. So, review logs and modify their settings to allow crawling.
In case you’re unsure if your security plugin is the problem, disable it temporarily and re-test access.
Also, we recommend requesting a list of blocked IPs from your hosting provider to confirm that Googlebot’s range isn’t affected. Ask if any automated security measures are interfering with Googlebot’s requests.
Step 7: Request Indexing
After you complete all these phases to fix the “Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)” error, validate the fix in GSC.
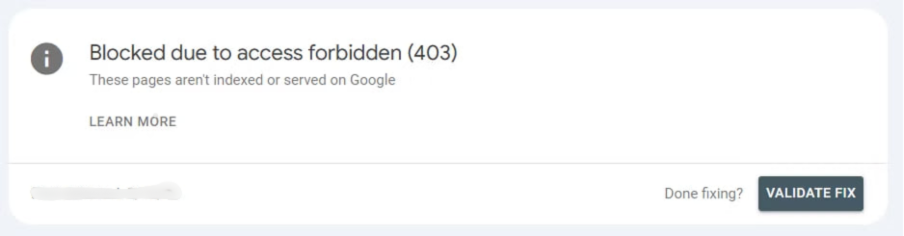
Then use the URL Inspection tool again to test if your changes were successful. Click on the “Request Indexing” button to speed up the processing of your site.
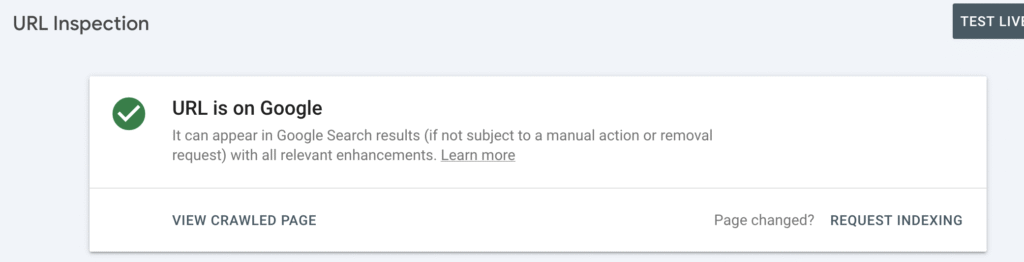
Visit your GSC from time to time to check the indexing status, as it may take some time.
If multiple pages were affected, consider submitting a new sitemap.xml with updated URLs.
Key Takeaways
- A “Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)” error in GSC can significantly impact your site’s visibility. If this status appeared unintentionally, you need to handle it without delay.
- Common causes for this error include robots.txt restrictions, server limitations, incorrect file permissions, etc.
- To resolve the problem:
- Locate the error in GSC;
- Confirm Googlebot’s access;
- Review your robots.txt file;
- Change unnecessary security settings;
- Fix file permissions and plugin limitations;
- Validate all changes in GSC and request indexing.
If you encounter other errors, refer to our Google Search Console guidelines to resolve them.

