Latest update: May 20, 2025
How Google Sees Your Site First, you need to understand how Googlebot — the search engine’s web crawler — scans and indexes your website. This guide breaks down how Googlebot works, why it’s important for SEO, and what you can do to make sure your site is fully optimized for crawling and indexing. No matter the size of your blog or e-commerce site, insights will help make your website more visible on search engine results pages.
What is Googlebot?
Googlebot (sometimes called a “spider”) is the web crawler software used by Google to discover and index web pages for its search engine. It systematically crawls the web, collecting data from websites and adding this information to Google based on Google ranking factors.
How Does Googlebot Work?
Googlebot starts with a list of known URLs from previous crawls and sitemaps, following links to discover new content. It downloads HTML and other resources, rendering pages (including JavaScript) using the Web Rendering Service based on Chromium. Website owners can influence its behavior with robots.txt file and meta tags, controlling which parts are crawled. The crawl frequency depends on the website’s update rate and server performance, determined by the site’s crawl budget.
Googlebot has specific technical properties, such as a file size limit of 15 MB for HTML and supported text-based files, applying to uncompressed data, with CSS and JavaScript fetched separately under the same limit, as per Google’s documentation. It supports protocols like HTTP/1.1 and HTTP/2, choosing the best for performance, and handles content encoding with gzip, deflate, and Brotli, ensuring efficient data transfer.
Verification of Googlebot is essential, especially given the risk of spoofed user-agents. Website owners can verify requests using reverse DNS lookup or matching IPs against Googlebot’s public IP ranges, updated as of December 24, 2024, according to Ahrefs. This verification process, detailed in Google’s documentation, is crucial for security and ensuring legitimate crawling activities.
How Googlebot Indexes the Web?
Googlebot indexes the web using a structured pipeline that ensures efficient discovery and accurate representation of web content. The process begins with a list of URLs that enter the Crawl Queue, from which the Crawler retrieves web pages. These pages then move to the Processing stage, where Google analyzes the content, checks for updates, and extracts any new links. Discovered links are returned to the Crawl Queue, feeding back into the pipeline for continuous crawling.
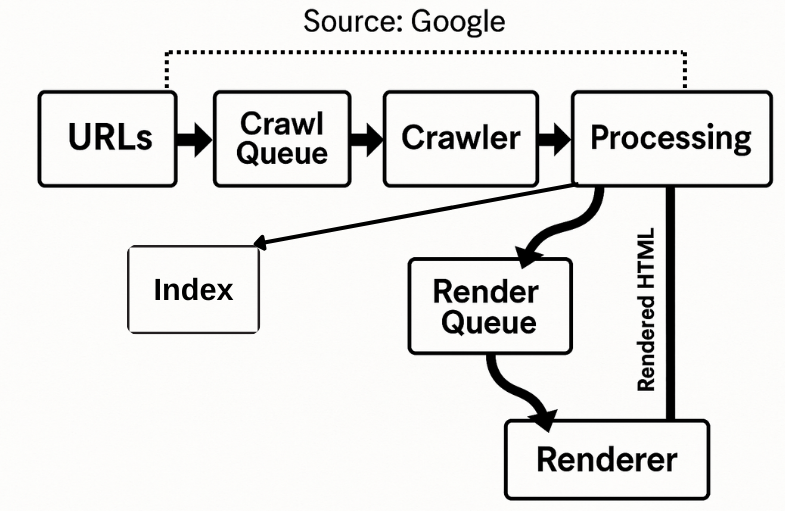
For pages that require additional rendering—especially those relying on JavaScript—the pipeline routes them through the Render Queue to the Renderer, which generates a fully rendered HTML version of the page. This rendered content is sent back to Processing to ensure complete understanding before being added to Google’s Index. Notably, Google indexes the mobile version of the rendered page, aligning with its mobile-first indexing approach. This pipeline ensures that Google maintains a fresh, comprehensive, and mobile-friendly index of the web.
How Often Google Bots Crawl Your Site?
Googlebot, crawl your site at varying frequencies depending on factors like how often you update content, your site’s authority (such as backlinks and domain age), and its technical health (like server response times). There’s no fixed schedule, but research suggests it can range from every few days for frequently updated sites to every few months for less active ones.
To find out how often Google is crawling your site, use the Crawl Stats Report in Google Search Console.
Common Issues with Googlebot Crawling
- Blocked by robots.txt;
- Slow-loading pages;
- Non-indexable content (e.g., Flash);
- Broken Links;
- Duplicate content.
What User Agent Does Googlebot Use?
Googlebot uses different user-agent strings depending on the type of content it’s crawling. The most common ones are:
- Googlebot Desktop – for desktop version of website;
- Googlebot Smartphone – for mobile version of website.
Below is a table of the Google bots most likely to visit your website.
| Crawler Type | User-Agent String |
|---|---|
| Googlebot (Desktop) | Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html) |
| Googlebot (Smartphone) | Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 6.0.1; Nexus 5X Build/MMB29P) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2272.96 Mobile Safari/537.36 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html) |
| Googlebot-Image | Googlebot-Image/1.0 |
| Googlebot-News | Googlebot-News |
| Googlebot-Video | Googlebot-Video/1.0 |
| AdsBot-Google | AdsBot-Google (+http://www.google.com/adsbot.html) |
| AdsBot-Google-Mobile | AdsBot-Google-Mobile (+http://www.google.com/mobile/adsbot.html) |
How to Manage What Googlebot Crawls and Indexes?
To effectively manage how Googlebot interacts with your website, it’s important to understand the tools and methods available for controlling what gets crawled. Google provides several options to influence crawling behavior. For instance, the robots.txt file allows you to block specific parts of your site from being crawled. You can also use nofollow attributes on links or meta tags to suggest that certain pages should not be crawled, which is useful for managing internal linking. Additionally, the Crawl Rate Control tool in Google Search Console enables you to adjust how frequently Googlebot accesses your site, helping to balance server load and crawl efficiency.
When it comes to controlling what gets indexed, there are a few key strategies. Deleting content is the most straightforward way to ensure it doesn’t appear in search results. You can also restrict access to certain pages with a password, preventing crawlers from viewing them. If you want a page to be crawled but not indexed, use a noindex meta tag. Lastly, Google Search Console’s URL Removal Tool allows you to temporarily prevent specific pages from being shown in search results, even though Googlebot may still crawl them. These tools give you granular control over your site’s visibility in Google Search.
Conclusion
If you know how Googlebot works, you can make smarter SEO decisions. If you manage crawl access, optimize page structure, and use tools like Search Console, you’ll be more likely to be indexed and ranked properly. If you make sure your site is set up just right, it’ll be easier for Google to understand, and it’ll show up higher in search results.
FAQ
A bot is a general term for automated software that performs tasks online, while a crawler is a specific type of bot that systematically scans and indexes web pages for search engines. All crawlers are bots, but not all bots are crawlers.
Googlebot can crawl millions of pages, but the amount it crawls from a single website depends on factors like site size, update frequency, server speed, and crawl budget. The crawl budget is the number of pages Googlebot is willing and able to crawl on your site, which is influenced by your site’s health and popularity.
No, Googlebot doesn’t “click” links or buttons like a human. Instead, it follows hyperlinks in the page’s HTML and may process JavaScript to discover dynamically loaded links. However, it doesn’t interact with elements requiring real user actions, such as logins, forms, or click-triggered content unless those elements are exposed in the rendered HTML or JavaScript.
Yes, modern Googlebot can render and understand JavaScript, thanks to its Chromium-based rendering engine.


